New high efficiency centrifugal extractor
 Extraction principle │ Example of extraction of phenol-containing wastewater by extraction | 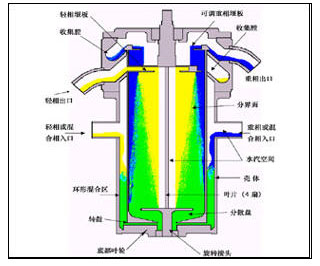
↑
Schematic diagram of direct-coupled centrifugal extractor
| Equipment overview
After the multiphase mixture having the difference in density enters the utility model, the mixed mass transfer process and the separation process are completed in the same machine. The direct-coupled motor drives the drum to rotate at a high speed through the coupling, which produces the powerful centrifugal force field required. By changing the motor speed through the inverter, the centrifugal force field can be changed to adapt to different systems. In this centrifugal force field, the multiphase mixture has different centrifugal forces due to its different density, and solid layering phenomenon is achieved, thereby achieving the purpose of extraction or separation.
|
| working principle:
The machine combines mixing and separation and is compact. The separation of the liquid-liquid two phases having a difference in specific gravity is accelerated by centrifugal force. The two liquid phases that are not fused enter the outer cavity of the rotor from the two feed nozzles, respectively, and are rapidly mixed by the rotation of the rotor. The mixed liquid enters the interior of the rotor through a passage in the bottom of the rotor. The interior of the rotor with self-priming pump function is divided into four vertical cavities, and the incoming liquids are balanced with each other. The liquid gradually separates during the flow from bottom to top in the rotor. The separation zone is from the baffle to the light phase, ensuring sufficient time to form a liquid-liquid interface. The separated liquid-liquid phase is collected into the respective collection chambers by light and heavy phases, respectively, and discharged from the respective outlets. The heavy phase raft can be removed and replaced to change the raft diameter.
Typical features:
◆Water phase or organic solvent mixture separation - maximum 2000mL / min, high efficiency, large processing capacity;
◆ Replace expensive intermediate storage tanks and pumps - multi-stage series countercurrent washing or extraction, saving equipment and land occupation;
◆Light and heavy phase two inlets - the minimum flow rate of extractant, solvent or detergent is 20mL/min, easy to use;
◆ Suitable for proportional, flow change and intermittent operation - research and development of ideal experimental equipment;
◆The size and speed of the sill plate are adjustable--suitable for liquid materials with different liquid specific gravity and different viscosity, and the application range is wide;
◆ Can provide FDA and cGMP-compliant models - easy to disinfect, CIP cleaning, quick-opening structure;
◆ Meet the application environment of explosion-proof and toxic and harmful media, sealed operation, no pollution to the external environment.
|
typical application:
This type of centrifugal extractor is widely used in liquid/liquid extraction or separation fields that do not contain solids or contain small amounts of solid systems. ?Such as:
◆ Oil-water separation (crude oil, heavy oil, diesel, etc., water removal, salt removal)
◆Pharmaceutical (such as using ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, n-butanol, chloroform, etc.)
◆ Chinese medicine extraction (tea extract tea toffee, Chinese medicine extraction garlic oil, etc.)
◆Pesticide (malathion and other extraction)
◆Bioengineering (nutrient solution, interferon extraction, etc.)
◆Chemical\Fine Chemicals (catalyst extraction, etc.)
◆Hydrometallurgy (using multi-stage extraction, stripping and other processes to extract rare metals such as nickel, copper, uranium, etc.)
◆Food (isolated or extracted from edible oil, spices, refined oil, food coloring, etc.)
◆Fragrance industry
◆Printing and dyeing industry (treatment and recycling of printing and dyeing wastewater)
◆Environmental protection industry (using multi-stage extraction, stripping and other processes, phenol-containing wastewater treatment, oil-water separation in ship sewage, oil-water separation, groundwater separation or extraction and purification, etc.)
◆The cosmetics industry (extracting nutrients, etc.)
◆Separation of liquid/gas two phases (removing bubbles from the liquid phase, etc.)
| 
↑
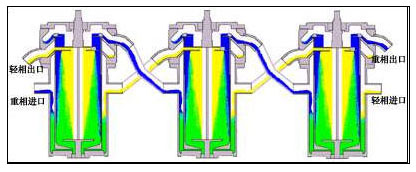
Easy to achieve multi-stage series countercurrent washing or extraction
| 
↑
CTL50-N extraction machine in application
| 
↑
CTL250-N direct-coupled centrifugal extractor
|
↑
|
Technical Parameters:
Project
Model
| Drum diameter mm | Mixed flux L/h | Motor voltageV/AC | Motor kW | import and export
Outer diametermm | Length × width × heightmm | quality kg | CTL50-N | 50 | 0 ~ 50 | 380 | 0.18 | φ17/φ17 | 280×240×720 | 50 | CTL70-N | 70 | 10 ~ 80 | 0.18 | φ17/φ17 | 340×280×755 | 65 | CTL150-N | 150 | 200 ~ 800 | 2.2 | φ34/φ34 | 495×495×1155 | 150 | CTL250-N | 250 | 800 ~ 3000 | 5.5 | φ50/φ50 | 725×725×1735 | 600 | CTL350-N | 350 | 3000 ~ 8000 | 11 | φ89/φ89 | 880×880×2100 | 1000 | CTL450-N | 450 | 8000 ~ 15000 | 15 | φ89/φ89 | 1100×1100×2250 | 1500 | CTL550-N | 550 | 15000 ~ 30000 | 30 | φ108/φ108 | 1300×1300×2750 | 2000 | CTL650-N | 650 | 30000 ~ 65000 | 30 | φ133/φ133 | 1500×1500×3200 | 3000 |
※ The above mixing flux is calculated as the flux of water. The data will change depending on the specific materials, whichever is the actual material.
Extraction principle
→ The operation of extracting one of the components from the liquid mixture with a solvent is called liquid/liquid extraction. Extraction is the use of the difference in solubility of the components in the solution in the selected solvent, so that the solute is liquid-liquid mass transfer to achieve the separation of the homogeneous liquid mixture. The entire extraction process can include:
1. The raw material liquid and the extracting agent are thoroughly mixed and contacted to complete the solute mass transfer process;
2. a separation process of the extract phase and the raffinate phase;
3. The process of recovering the extractant from the extract phase and the raffinate phase. It is usually recovered by distillation.
→ The extraction operation is illustrated by taking the A component in the mixture containing the two components A and B as an example. A suitable solvent S is selected which has a significant solubility for the component A to be extracted, and which is completely insoluble or partially miscible with respect to the other component B (the smaller the mutual solubility, the better). The solvent S selected is referred to as an extractant. The mixed liquid to be separated (containing A+B) is referred to as a raw material liquid, wherein the extracted component A is referred to as a solute, and the other component B (a raw solvent) is referred to as a diluent.
Three steps of the extraction process:
(1) First, the raw material liquid (A+B) is thoroughly mixed with an appropriate amount of the extractant S in a mixer. Since B and S are not miscible, there are two liquid phases of S and (A+B) in the mixer. Stirring is carried out to cause a large phase interface, and the two phases are sufficiently contacted, and the solute A is diffused from the raw material liquid (diluent B) through the phase interface to the extractant S. Thus, the concentration of A gradually decreases in the liquid phase of the raw material, and gradually increases in the liquid phase S. After a certain period of time, the concentration of A in the two phases no longer changes with time, which is called extraction equilibrium.
(2) After sufficient mass transfer, due to the difference in density between the two liquid phases, stratification may occur by standing or by centrifugation, thereby achieving the purpose of separation. One phase mainly containing the extractant S and having more solute A is called the extract phase, and is represented by E; a phase mainly composed of the diluent B and containing a small amount of undiffused solute A is called a raffinate phase, and is represented by R. .
(3) S is usually recovered by distillation. The extracted phase after removal of S is referred to as an extract; the raffinate phase after removal of S is referred to as a raffinate.
| Light and heavy

Treatment of p-nitrophenol sodium phenol wastewater by centrifugal extraction
Waste water is produced during the production of chemical products. Such as product washing wastewater, production plant equipment and ground washing wastewater. These wastewaters are collected and discharged into rivers, rivers and lakes through sewer pipes. When the various harmful components contained in these wastewaters reach a certain concentration, they will cause serious pollution to rivers, rivers and lakes. The consequences are damage to the ecological environment and the physical and mental health of the people. Such as phenol-containing wastewater produced by the steel industry coking plant; nitrification wastewater produced by chemical production enterprises, nitrophenol wastewater; phenol-containing wastewater produced by the lumber mill. The concentration of phenol in these wastewaters is generally about 1000 to 5000 ppm. Some can reach 10,000ppm. If the phenol contained in such wastewater is taken out, the discharged wastewater is up to standard, that is, the pollution to the environment is alleviated, and the extracted phenolic product can be reused in production, which has certain economic benefits.
CTL325-N centrifugal extractor is a new generation centrifugal extractor developed by our company's scientific research personnel for the research and development of metal uranium extraction equipment for the defense industry. The machine integrates mass transfer and separation, and has the characteristics of compact structure, large processing capacity, stable operation, low power consumption, convenient cleaning and maintenance. Can be used stand-alone or multi-machine series. According to different extraction systems and conditions of use, the parameters of the rotation speed, the diameter of the blade and the diameter of the heavy phase plate are adjusted to improve the mixing degree, separation effect and extraction efficiency of the two phases during extraction.
Taking 4,000 tons of sodium p-nitrophenolate as an example, the corresponding wastewater discharge is about 20,000 m3 per year. The design is 70m3 per day, 300 days per year, and the annual treatment of phenol-containing wastewater is 21000m3. It can completely dispose of the phenol wastewater contained in the production, completely solving the problem of phenol wastewater discharge.
Production process of sodium p-nitrophenolate: 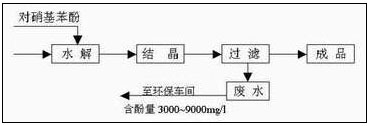
One. Design Parameters
1. Treatment scale: According to the amount of water, it is operated for 300 hours per day for 14 hours per day. The amount of water treated per day is 70m3, and the amount of water treated per year is 21000m3.
2. Program selection and process conditions:
The solution adopts centrifugal extraction technology and three-stage countercurrent extraction using a large-capacity centrifugal extractor, and the three-stage countercurrent back extraction can achieve the best dephenolation effect and the effective regeneration and recycling ability of the extractant. After the phenol-containing wastewater is treated, the dephenolized wastewater discharged contains phenol content <10ppm, volatile phenol content <0.5ppm, extraction ratio: wastewater and extractant is 3:1~4:1; back extraction ratio: extractant and The lye is 2:1 to 3:1; the specific parameters are determined after the test. The centrifugal extractor drum is made of 316L; the casing part is made of polypropylene sheet and has reliable corrosion resistance.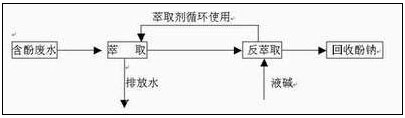
| Brief description of the process: the phenol-containing wastewater is sent to the centrifugal extractor. At the same time, the extractant enters the centrifugal extractor in proportion, and the wastewater is discharged to the centrifugal extractor after extraction and dephenolization. The phenol-containing extracting agent enters the stripping machine while the liquid alkali enters the stripping machine in proportion to the alkali washing operation of the phenol-containing extracting agent, and the extracting agent can be recycled after the alkali washing. After stripping, a sodium phenolate solution is discharged from the stripping machine for sodium phenol recovery. The extractant is made of ABK complex extractant, and the liquid base is prepared by industrial caustic soda.
three. Equipment configuration and process
The scheme selects three-stage extraction and three-stage stripping process. The main equipment is 6 centrifugal extracting machines and equipped with corresponding auxiliary equipment such as tanks, tanks and pumps. The process is simple and easy to operate. See the flow chart for details.
Brief description of the process:
1. Waste water: The phenol-containing wastewater is sent to the wastewater sedimentation tank by pump or pipeline for use. The sedimentation wastewater is pumped into the high-level tank of the waste water. When the high-level tank is filled, the excess waste water is returned to the sinking tank through the overflow pipe. At this time, the pump stops. run.
2. Extractant: For the convenience of visual description, we will abbreviate the extractant as net oil before and after stripping; it will be called phenol oil after extraction and back extraction. The net oil is stored in the storage tank and pumped into the high oil tank of the net oil. When the high level tank is filled, the excess net oil is returned to the storage tank from the overflow pipeline, and the pump stops running.
3. Liquid alkali preparation: The concentrated alkali (30%) and tap water are added to the alkali tank and stirred to prepare 10%~15% dilute alkali solution for use. The dilute lye is pumped into the liquid alkali high tank 3. When the high tank is full, the excess liquid alkali is returned from the overflow pipeline to the alkali tank, and the pump stops running.
4. Extraction and stripping operation: During the extraction operation, the phenol-containing wastewater and the net oil are fed into the extraction machine from the respective high-level tanks through the flow meter, and the wastewater is first entered by the 3# machine. The net oil enters the countercurrent from the 1# machine. extraction. After three-stage countercurrent extraction, the dephenolized wastewater is discharged into the buffer tank by the 1# machine, and the dephenolized water can be discharged to the sewer after the micro-oil collection (concentrated discharge after neutralization). The trapped phenol oil is recycled and reused; the phenol oil flowing out from the 3# machine is heated by the heat exchanger to enter the 4# machine for stripping operation, and the liquid alkali is proportionally entered by the high-level tank through the flow meter and the heat exchanger. The machine performs a stripping operation. After stripping, the net oil is discharged from the 6# machine into the buffer tank and separated by oil and water. The pump is discharged through the cooler and returned to the net oil storage tank for recycling. After the stripping, the phenol sodium liquid is discharged from the 4# machine into the buffer tank for oil-water separation. Thereafter, the bottom of the sodium phenolate right buffer tank is discharged to the phenol product recovery unit. The net oil obtained after the separation of oil and water can be concentrated and reused. |
Previous:Nothing
Next:Nothing
|


 CN
CN EN
EN





